Orthogonal Intercepts probe
You can use this probe to estimate membrane thickness (e.g., thickness of the interhemal membrane in the placenta that separates the maternal from the fetal blood).
Isotropic thin sections are required for this probe.
The program displays a grid over the tissue. You will use the grid to make a series of length measurements along the membrane so that thickness can be estimated. More specifically, when a membrane wall intersects with the grid (black circle in the figure below), measure the length. To measure the length, draw a line-segment (blue line with arrow head in the figure below) between the intercept and the other wall of the membrane ensuring that the line meets the other wall orthogonally; this will be the shortest distance across the membrane in that particular section.
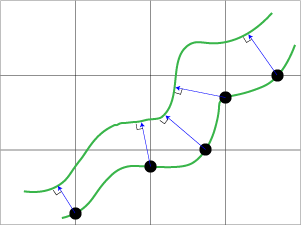
Although the tissue orientation is isotropic, the thickness is likely to be overestimated since not all sections will be perpendicular to the membrane surface (i.e., non-perpendicular cases of sectioning will cause the thickness to appear longer). To correct for this, we report additional estimates calculated as follows:
- Estimate using harmonic mean: T= Harmonic mean multiplied by 8/3π
- Estimate using arithmetic mean: T= Arithmetic mean multiplied by π/4
We recommend that you consult this article by Coan et al. to understand how thickness is estimated and what numbers are most relevant to your research.
Size must be defined via Probes>Define counting frame before starting the probe (see procedure below).
Placement must be defined via Probes>Preview SRS layout before starting the probe (see procedure below).
The SRS grid size should be set to sample an appropriate number of sites per section to achieve the required precision. The distribution of the objects of interest will dictate the grid size.
Grid spacing should be set to optimize precision. Learn more about area and thickness sub-fractions here.
Procedure
- Place a reference point.
- Optional: Use the Serial Section Manager to keep track of the sections that should be obtained via systematic random sampling.
- Trace the region(s) of interest at low magnification (i.e., with low precision). See Tracing contours.
- Select a lens so that you can see the membrane clearly.
- Click Probes>Define Counting Frame and define the counting frame size.
- Click Probes>Preview SRS Layout to estimate the grid size (see Determining Sampling Precision). Right-click and select End preview mode to turn the preview off.
- Click Probes>Length>Orthogonal Intercepts.
- Adjust the probe settings and click OK. The program displays a grid.
- Measure within the site by drawing a series of line-segments.
- Starting at a point where the grid and the membrane wall intersect (black circle in the figure), click and drag the mouse to the other membrane wall so that line-segment (blue line with arrow head in figure) and wall meet orthogonally.
- Release the mouse. A blue line has been drawn.
- Repeat steps a and b as necessary to draw more line-segments.
To delete the last line-segment drawn, press CTRL-Z.
- Starting at a point where the grid and the membrane wall intersect (black circle in the figure), click and drag the mouse to the other membrane wall so that line-segment (blue line with arrow head in figure) and wall meet orthogonally.
- Right-click and select next scan site and repeat step 9.
- Repeat step 10 until you've visited all the sites.
- To view the results, click Probe run list: Harmonic mean, estimate using harmonic mean, arithmetic mean, estimate using arithmetic mean, and measured lengths are reported.