Area Fraction Fractionator probe
Purpose

The Area Fraction Fractionator (AFF) is essentially a Cavalieri point counting estimate of area and volume performed on a systematically selected fraction of the tissue.
The probe is designed to estimate the fraction of a region occupied by a sub-region. Any number of sub-regions may be examined using the AFF. This area fraction probe is implemented by performing a fractionator scan of the area of interest, while overlaying a grid of points (as in the Cavalieri estimator).
Examples for use:
- Comparing the ratio of white matter to gray matter in the spinal cord
- Quantifying the ratio of muscle fiber to connective tissue to vasculature in a muscle
A shortcoming of the method is that there may be uncertainty in judging whether points near the boundaries of the area are inside or outside of the region of interest or object of interest.
Counting frame size
Size is defined via Probes>Define counting frame before starting the AFF (see procedure below).
The counting frame should be sized so that it is large enough to distinguish between the regions of interest within the counting frame. A general rule of thumb is that the counting frame is 1/3-2/3 of the field of view used for viewing the objects of interest.
XY placement of counting frames
Placement is defined via Probes>Preview SRS layout before starting the AFF (see procedure below).
The fractionator scan grid size should be set to sample an appropriate number of sites per section to achieve the required precision. The distribution of the objects of interest will dictate the grid size. Larger grid sizes will save time, but the grid size must be small enough that it will not skip over any important region of the tissue.
Cavalieri settings
Grid spacing: Enter a value.
The smaller the distance between lattice grid points, the more accurate the estimate. However, using too many points can be inefficient because it increases the time spent on each site.
Markers
Left button marker: Left button refers to the standard left mouse button.
Middle button marker: Middle button refers to the mouse wheel button on a standard mouse.
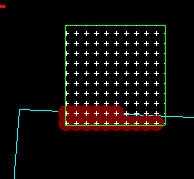
Mark points inside contour: When selected, automatically marks all points that are both inside a counting frame and the contour (dark red disk in the example).
- Next scan site: Advances you to the next site.
- Previous scan site: Returns you to the most recent site where you marked points.
- Paint mode: Default marking mode. Use to mark groups of adjacent points.When in Paint mode, hold the ALT key to erase the selected marker
- Erase current marker mode: Click a marker in the site to delete it. You can only delete markers of the currently selected marker type (e.g., delete green triangles one at a time if you just marked with the green triangle marker type). To return to marking, right-click and select Paint mode.when in Erase mode, hold the ALT key to place markers.
- Clear site: Removes all the markers placed in the current site.
- Preview area fraction: Provides a bird's-eye view of all markers. To leave the preview, right-click and select End preview mode.
Go to File>Preferences>AutoSave to set your AutoSave settings to minutes instead of number of data points.
- Place a reference point.
- Define your sections with the Serial Section Manager. The Section Cut Thickness is used to calculate the estimates. You need to know the interval between the sections to be sampled.
- Trace the region(s) of interest at low magnification (i.e., with low precision). SeeTracing contours.
- Select a lens suitable to mark the tissue.
- Click Probes>Define Counting Frame and define the counting frame size.
- Click Probes>Preview SRS Layout to estimate the grid size (see Determining sampling precision). Right-click and select End preview mode to turn the preview off.
-
 Go to Probes > Volume/Area and click Area Fraction Fractionator to open the Area Fraction window.
Go to Probes > Volume/Area and click Area Fraction Fractionator to open the Area Fraction window. - Counting frame size and XY placement of counting frames display the dimensions you specified in Step 5.
- Cavalieri settings: Enter a grid spacing for the distance between points. The grid can also be rotated randomly.
- Select marker types:
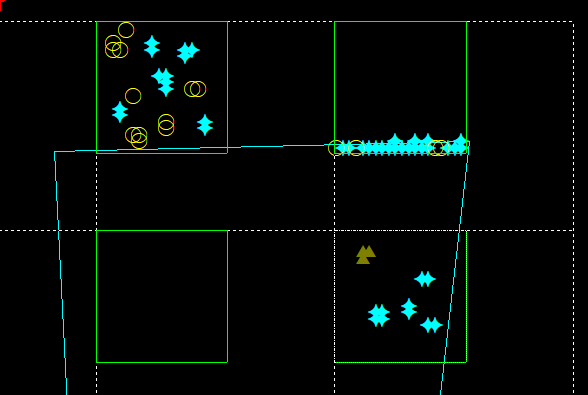
- Left Button Marker (Left Button refers to the left mouse button): Used to mark single points or groups of adjacent points for the sub-region (e.g., plaque, lesion). You will mark the grid points that meet these 2 criteria: 1) they appear on the objects or region of interest, and 2) they are contained by the counting frame.
- Middle Button Marker (Middle Button refers to the mouse wheel button): Used to fill the region of interest, that is, area of the contour overlaid by the counting frame (e.g., cortex). You will mark the grid points that meet all 3 criteria: 1) they appear in the region of interest, 2) they are contained within the counting frame, and 3) they do not appear on the objects of interest.
- Optional: Check Mark points inside contour: all points found in both the counting frame and the contour are automatically marked with a third marker type (dark red disk in the example).

Counting objects
- Mark regions of interest: Make sure to adjust the size of your cursor with the mouse wheel (otherwise, you might not see the markers you're placing).
- To fill the entire area inside the contour with Middle Button Markers (cf. Step 7), click the mouse wheel button.
- To mark a single point, left-click once.
- To mark several adjacent points, drag the mouse (Paint mode) or use the Marquee mode: right-click, select Marquee mode then drag the mouse across the area of interest; a white rectangle is drawn and all points within that rectangle are marked.
To measure the area fraction of several types of objects, use additional marker types, one marker type for each region of interest.
Select a marker type from the Marker toolbar then left-click to place a marker.
Repeat with a different marker type for each region of interest. - When you are finished marking, right-click and select Next Scan Site.
To return to the previous site, right-click and select Previous Scan Site.
- Repeat the Steps 8 and 9 until all sites have been visited.
- If you have multiple sections, move to the next section and repeat Steps 8–12.
-
 To view the results, use Probes>Probe run list.
To view the results, use Probes>Probe run list.
- Area Fraction (click Markers on the left): Fraction of tissue (region) occupied by the sub-region (plaques)
- Estimated Area (click Markers on the left): Area of tissue (region) occupied by the sub-region (plaques)
- Planimetry: Area and volume of the region of interest based on the traced contour.
- CE (available if you've done at least three probe runs)