Nodes (branched structure)
|
Use to compile the location of nodes on processes (dendrites or axons). |
Analysis results
Each tree selected for the analysis is assigned a unique number starting at 1.
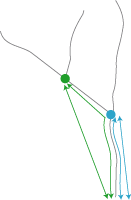
Describes the node position based on its root segment. The root segment is the segment closest to the origin of the process; the other segments are referred to as daughter segments.

|
R is the root segment, that is, the segment from the origin to the first node. In a bifurcating tree, the daughter segments at the first node are R-1 and R-2.
|
Length of the path from the origin to the node.
Shortest distance from the origin to the node.
Tortuosity = [Distance along process] / [Straight line distance]
- The smallest tortuosity possible is 1—This is a straight path.
- Tortuosity increases as the segment assumes a more complex path to reach its destination.
- Tortuosity allows segments of different lengths to be compared in terms of the complexity of the paths they take.
(X,Y,Z) coordinates of the node