ApoTome setup
Requires a separate license
The settings you select depend on the tissue and its preparation, your study, and the time frame. In general, settings that increase the image quality also decrease the image acquisition speed. After the initial setup, you are most likely to use this window to change the grid (see Grid Insert below) or to use image filters (see Image Filter options below) to obtain more appropriate optical sections and image quality. 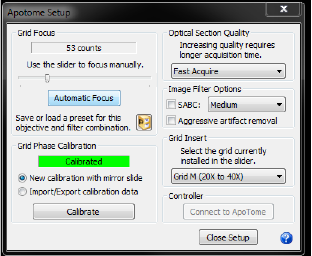
The ApoTome uses the full dynamic range of the image. Changing the black point and white point will improve the live image preview, but will have no impact on the final image. 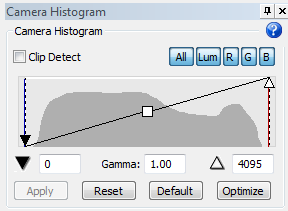
Click Connect to connect to the ApoTome.
Grid focus is defined during the initial setup. Adjust it only if you notice that the quality of ApoTome images has declined (i.e., grid lines are visible with SABC enabled, or the image is grainy despite an appropriate dynamic range.
It is different for each objective and filter you use.
- Slider: Use the slider to manually focus the ApoTome grid in the light path until you find a position where the grid lines are sharpest in your live image. The program displays the number of counts used.
- Automatic Focus: The program starts the automatic focus procedure and displays a number of counts.
- Presets: Save presets for objective/filter combination; they are required for the Device Command Sequences; use an existing preset to move quickly to a previously saved focus position.
For best results, identify and save the best grid focus for each objective and fluorescent filter combination to be used for the initial setup. Loading presets for particular combinations is faster and easier than searching for the best focus each time you change the filter or objective.
There are three grids available named after the magnification level they are most appropriate for: Low (grid L), Medium (grid M) and High (Grid H).
Generally, we recommend Grid L at 10X, Grid M at 20X-40X, and Grid H at 63X-100X. Note that Grid M is sometimes used to achieve a thinner optical section at higher magnification, such as 63X. Increase the dynamic range of your image before changing grid.
Note that the grid insertion process is different for ApoTome 1 and ApoTome 2:
- ApoTome.1: If you manually changed the grid in the slider, use the drop-down menu to select the corresponding grid from the list.
- ApoTome.2: To change the grid in the slider, use the drop-down menu to select the desired grid. The grid is installed automatically.
Calibration is done during the initial setup. Adjust it only if you notice that the quality of ApoTome images has declined (i.e., individual calibrations fail while all other settings are suitable).
To re-calibrate, use the calibration slide and filter and select New calibration with mirror slide.
To back up successful calibrations, select Import/Export calibration data and click Import or Export.
Acquired images may have artifacts burned (or "bleached") into the tissue from the acquisition process. We provide two options to eliminate such artifacts.
- SABC (Spatially Adaptive Bleaching Correction): SABC is a mathematical post-processing algorithm that corrects for differences in illumination and removes grid lines from the image. Most of the time, it’s safe to set this to medium and never worry about it again. Setting it to high can potentially introduce artifacts into the image.
When to use it
The tissue between grid lines gets bleached during acquisitions, especially during those with long exposure times. However, areas under the shadow of the grid are protected from bleaching. Basically, the areas between the grid lines are bleached into each image, resulting in uneven illumination. When the grid moves, the area that was just protected by the shadow of the grid lines is imaged. Under some conditions, especially at higher magnifications with grid M, this introduces artifacts into your image.
- Aggressive artifact removal: Use to remove the most stubborn artifacts. It is highly unlikely that you'll need this option. If you decide to use it, however, do so with extreme caution as it may remove some of your sample from the image.
To increase quality, use more input images. Increasing the image quality can reduce grid line artifacts and reduce noise similar to averaging images, but it requires a longer acquisition time.
- Fast Acquire—3 input images acquired to create the single, final image.
- Good Quality—5 input images
- Better Quality—7 input images
- Best Quality—9 input images
Also see ApoTome: Acquire a stack and create a projection image, Troubleshooting ApoTome acquisitions