Explosions can tear apart buildings, send shrapnel flying, and hurtle humans into the air. But explosions also cause damage in ways that aren't as visually apparent. Scientists say the force of a blast can cause brain damage, but questions linger about how the symptoms that emerge after a blast-induced traumatic brain injury are connected to the initial trauma. In their quest to learn more about how symptoms...
Read More
MBF Bioscience Blog
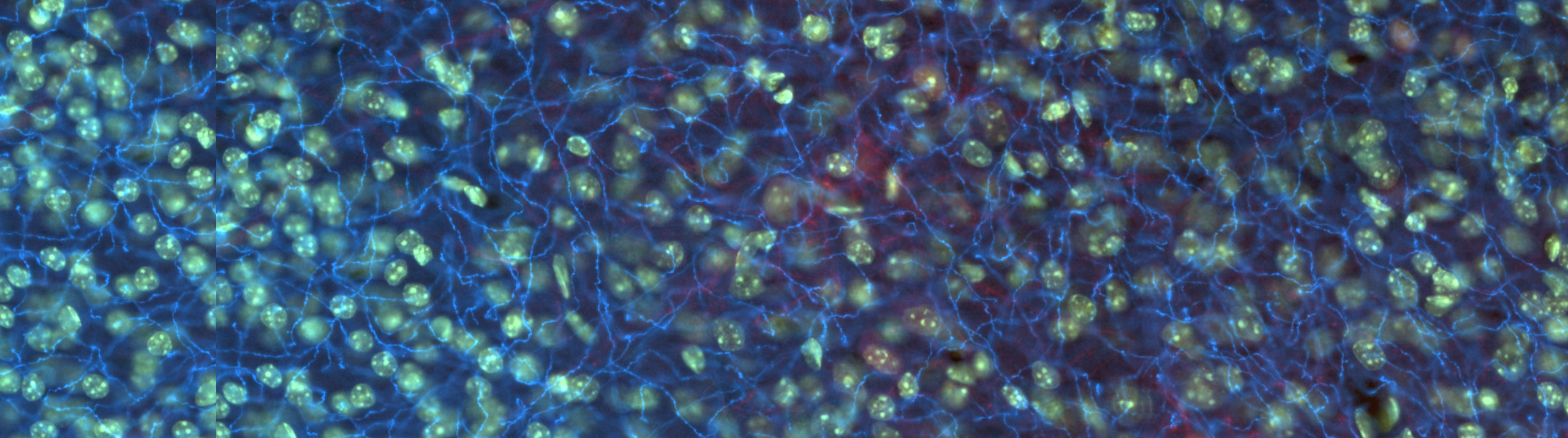
[caption id="attachment_5991" align="aligncenter" width="632"] Dr. Paul Manger's new system developed by MBF Bioscience for analyzing large mammalian brain specimens[/caption] Dr. Paul Manger, Research Professor at the University of the Witwatersrand, South Africa, studies the brain anatomy of various animals to better understand the relationship between brain structure and function. Some of the mammals he studies have very large brains that don't fit under a conventional research...
Read More[caption id="attachment_5635" align="aligncenter" width="584"] Representative dendrites of dentate gyrus neurons of Siberian hamsters injected with melatonin (stained with Cresyl violet). Ikeno et al found hamsters injected with melatonin displayed decreased spine density on neurons in the dentate gyrus. Image courtesy of Tomoko Ikeno, Ph.D.[/caption] Night falls and a powerful hormone called melatonin kicks in. The gears of the circadian clock are turning as you get ready...
Read MoreIn 2014 researchers used Stereo Investigator in 698 peer-reviewed papers - citing it almost three times more than all other stereology systems combined. Researchers tell us they use Stereo Investigator because: it works with many different microscopes and imaging technologies it provides unbiased data about neuron populations and regions of interest it comes with strong technical and research support provided by MBF Bioscience [caption id="attachment_5790" align="alignnone" width="1394"] source: google scholar[/caption] Dr. Mark West, co-developer of...
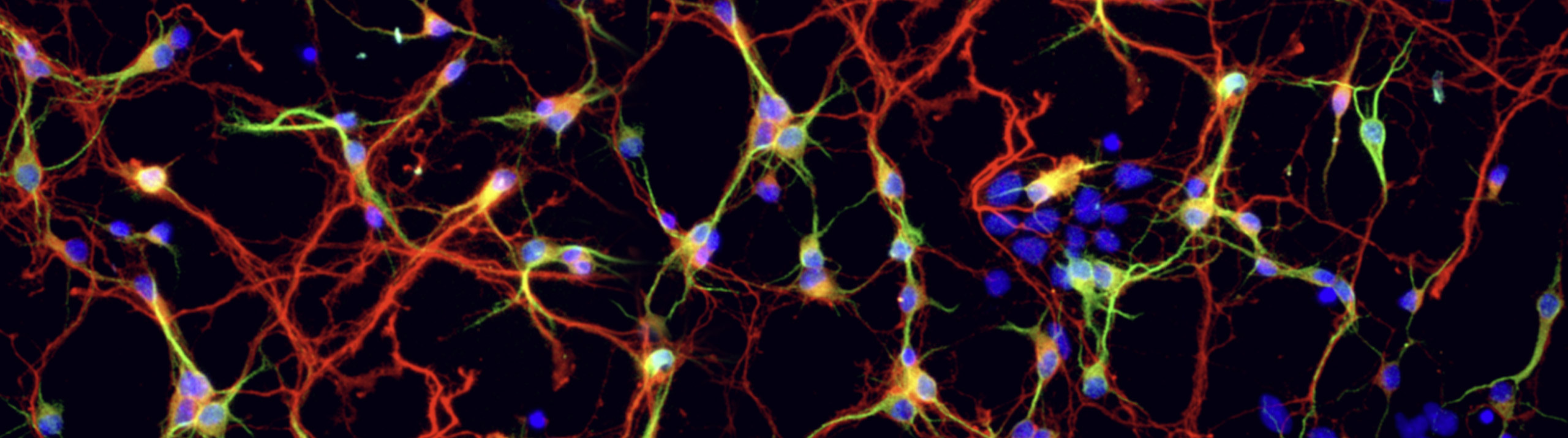
Read More[caption id="attachment_5546" align="aligncenter" width="401"] A representative confocal image of spinal cord tissue fluorescently immunolabeled for SC121 (red) in conjunction with GFAP (green) – markers that allowed researchers to quantify stem cell differentiation and migration. (Image provided by study author Dr. Aileen J. Anderson)[/caption] Research has shown that transplanting human neural stem cells into damaged spinal cords restores locomotor function in a mouse model of spinal cord injury1. Researchers...
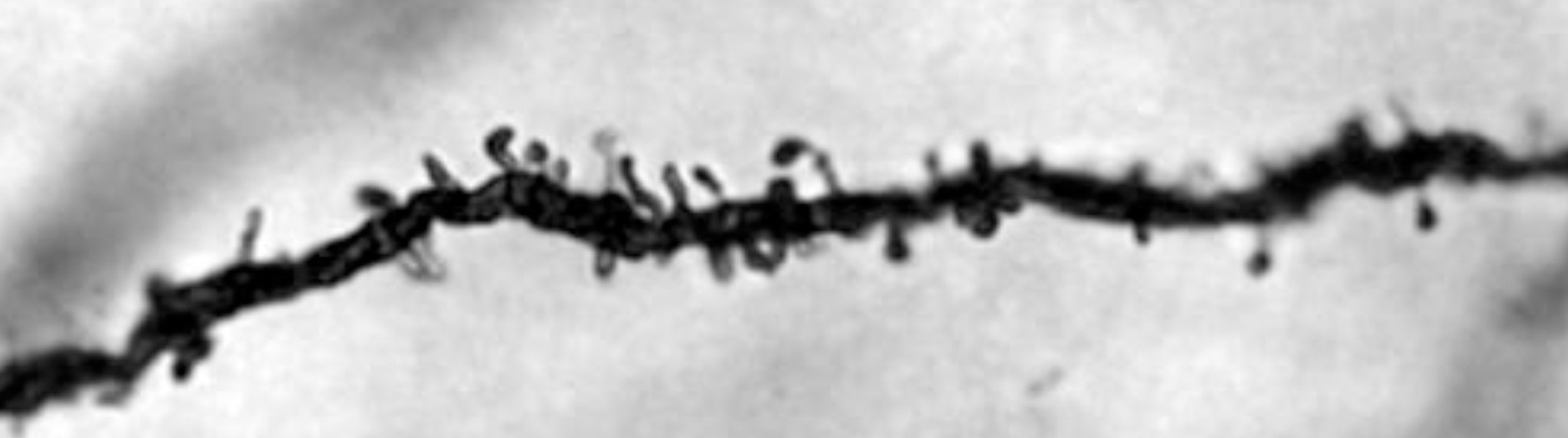
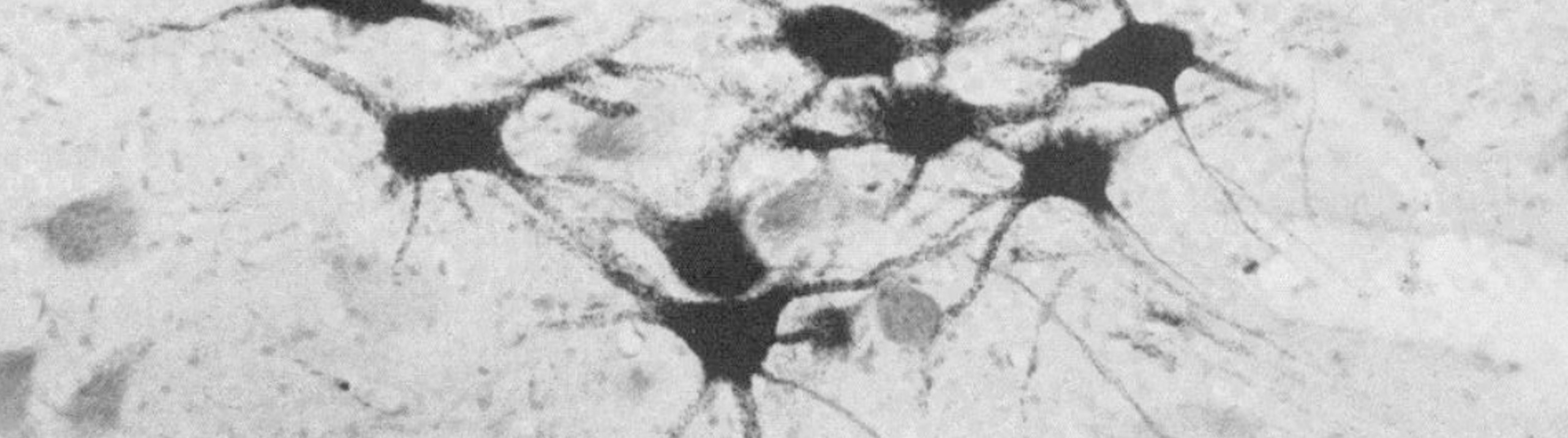
Read More[caption id="attachment_5745" align="aligncenter" width="307"] Golgi-stained human brain tissue from the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex.[/caption] Schizophrenia and bipolar disorder are very different mental illnesses, but researchers are discovering evidence that the two disorders have some common pathologies. According to a recent study, a shared characteristic appears to be dendritic spine loss. The researchers used Neurolucida to study pyramidal cells in human brain tissue from individuals with schizophrenia (n=14), individuals with bipolar...
Read More[caption id="attachment_5670" align="aligncenter" width="210"] Drs. May-Britt and Edvard Moser Image from GEIR MOGEN / NTNU[/caption] Drs. May-Britt and Edvard Moser were awarded the 2014 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for discovering the cells that form a network for spatial navigation in the brain, and we're proud to say they are MBF Bioscience customers and used Neurolucida in their research. In 2006, the Norwegian husband and wife...
Read More[caption id="attachment_5617" align="alignnone" width="700"] This image stack was used in the study to analyze spine density. Image courtesy of Tara Chowdhury, Ph.D. first author of the study.[/caption] To find out how anorexia nervosa changes the brain, scientists at New York University are studying a rat model of the disease called activity-based anorexia (ABA). Previously, they discovered that ABA rats develop unusually robust dendritic branching of neurons...
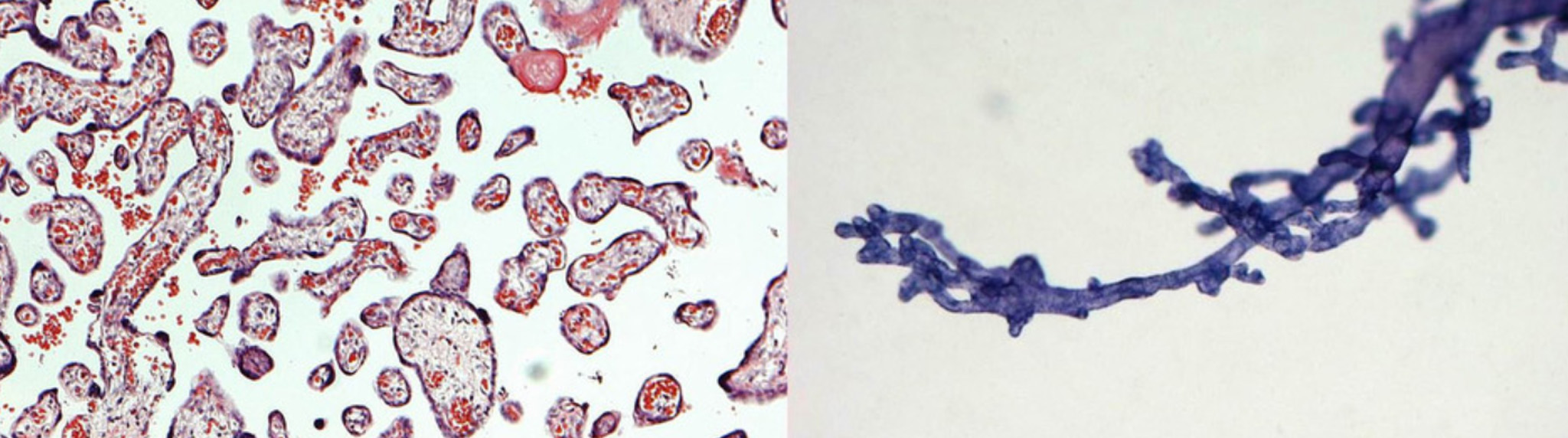
Read MoreWhen neuroscientists started studying neurons in 3D, it revolutionized brain science. Now, for the first time, scientists are using this same technology to study the human placenta, and they've made some fascinating new discoveries about its structure. Using Neurolucida to create 3D reconstructions of villous trees – three-dimensional structures in the placenta that facilitate gas and nutrient exchange between the fetus and mother – researchers in...
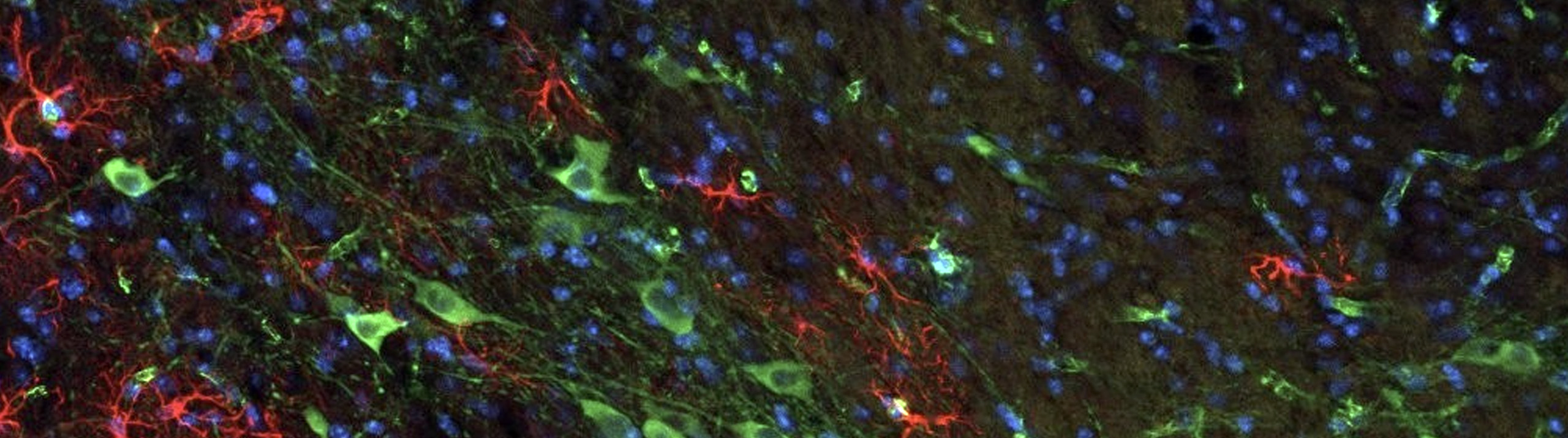
Read More[caption id="attachment_5560" align="aligncenter" width="800"] Almeida-Suhett et al saw delayed loss of GABAergic interneurons in the BLA within the first week after mild CCI. (Representative photomicrographs of GAD-67 immunohistochemically stained GABAergic interneurons in the BLA of sham (left), 1-day CCI (middle), and 7-day CCI (right) animals. Total magnification is 630x; scale bar, 50 µm.)[/caption] Soldiers, athletes, and other individuals who suffer a traumatic brain injury often develop...
Read More