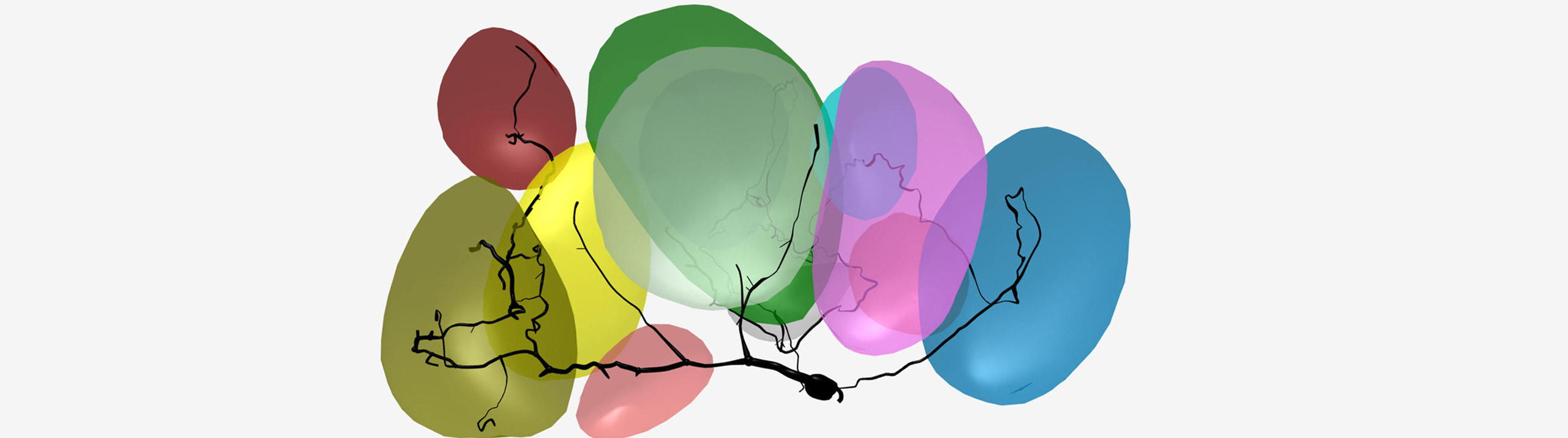
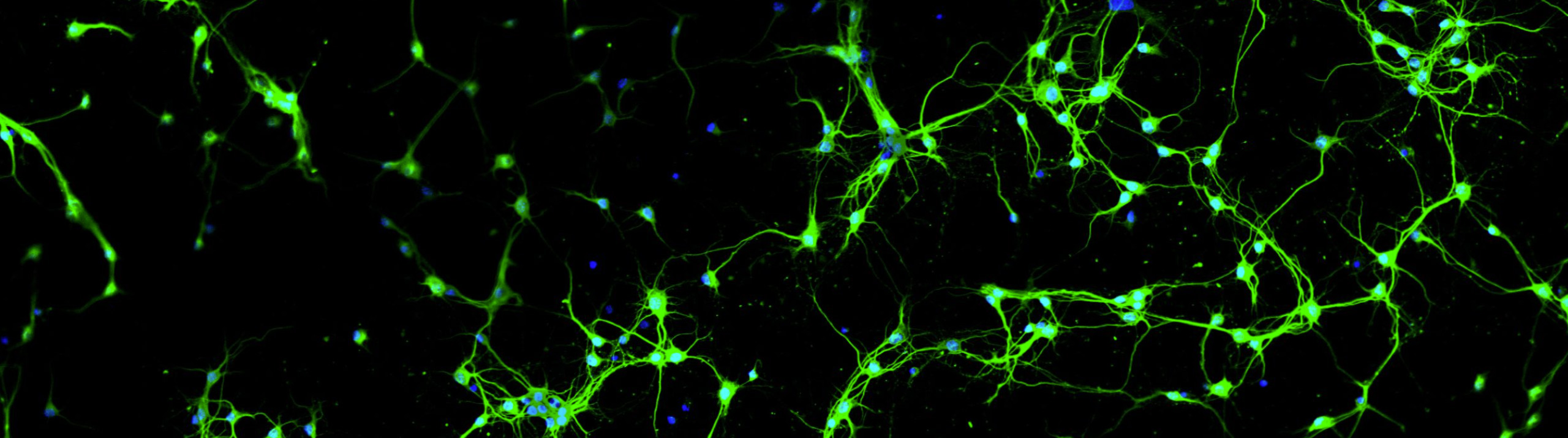
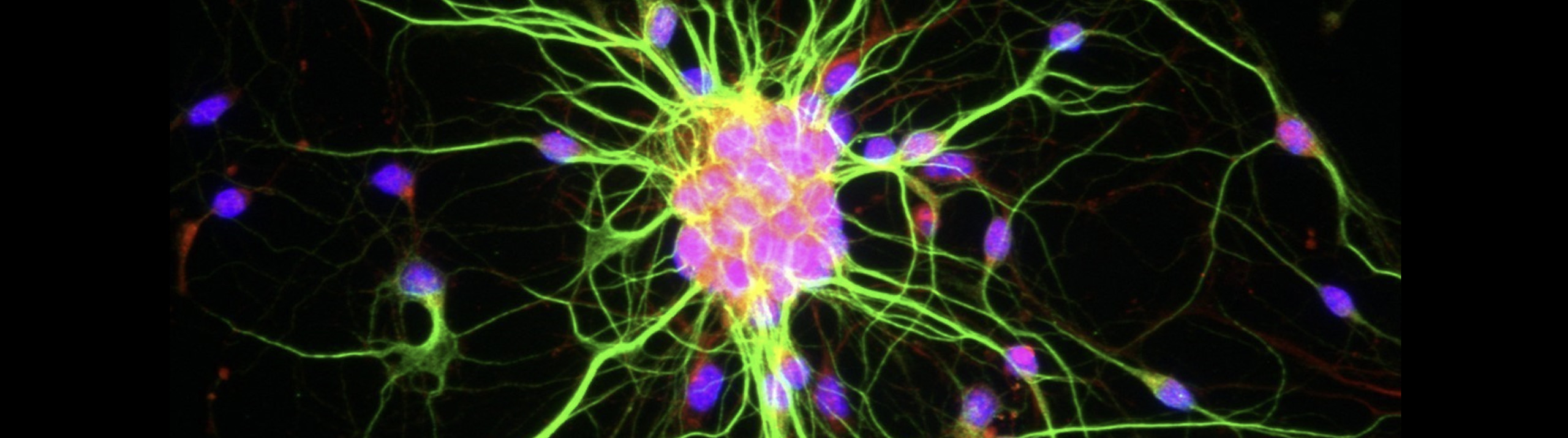
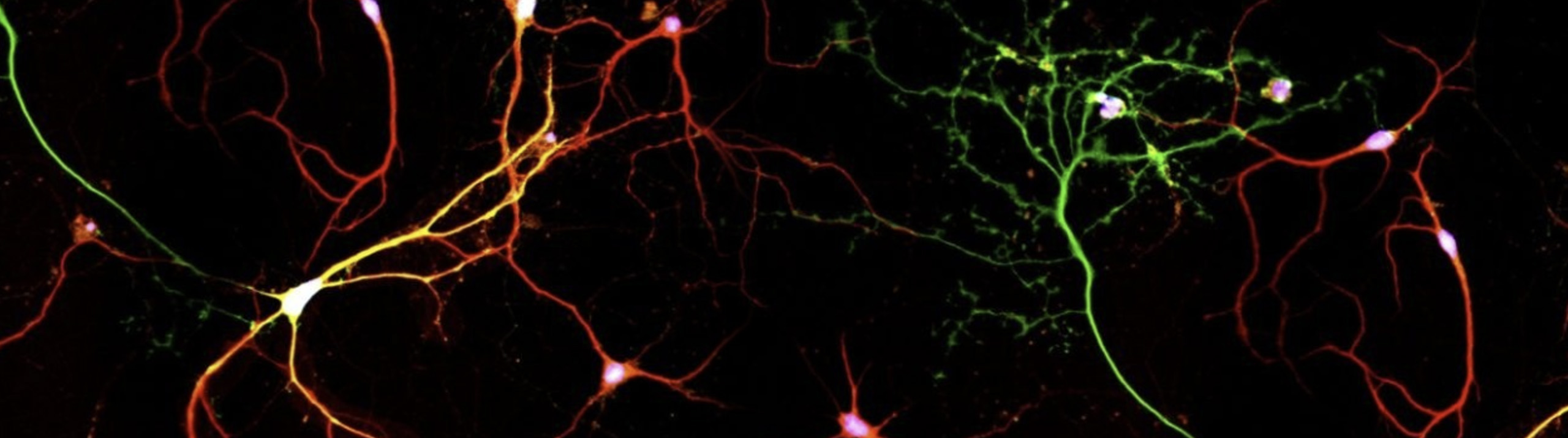
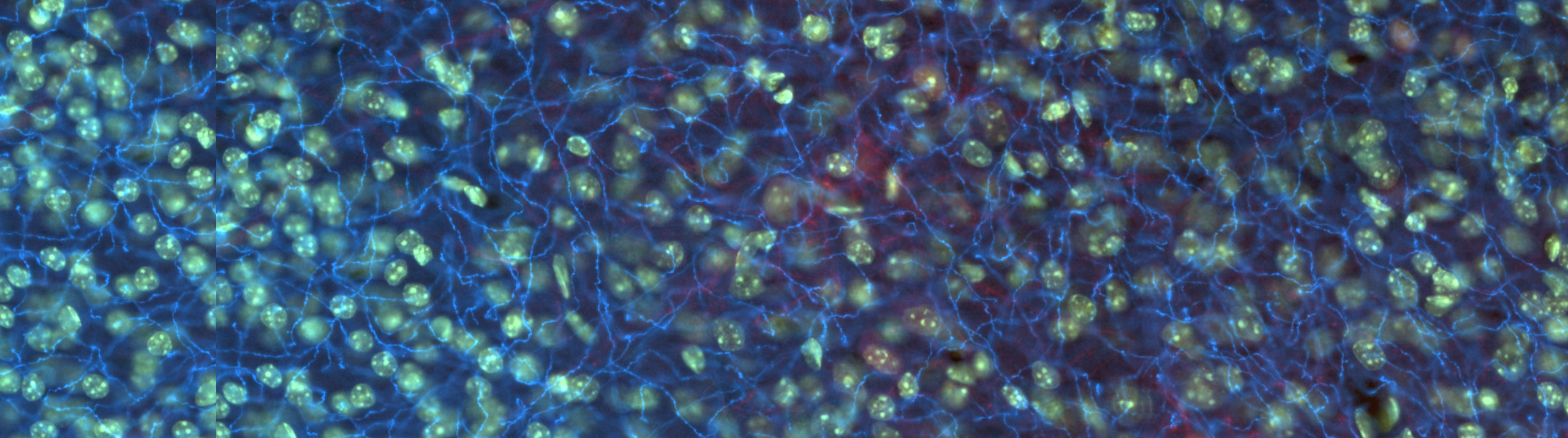
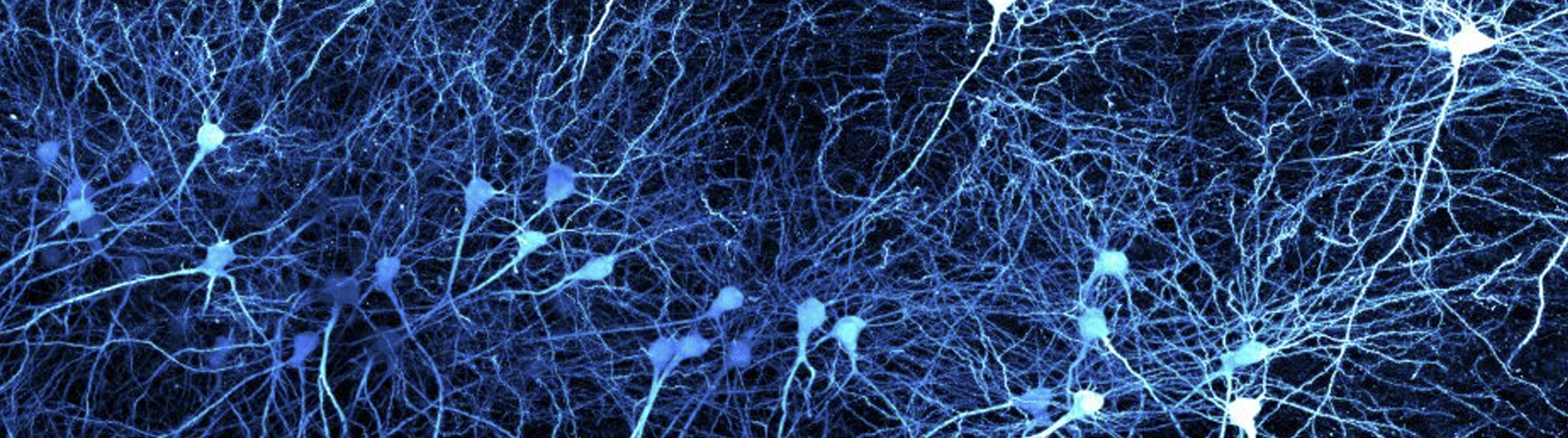
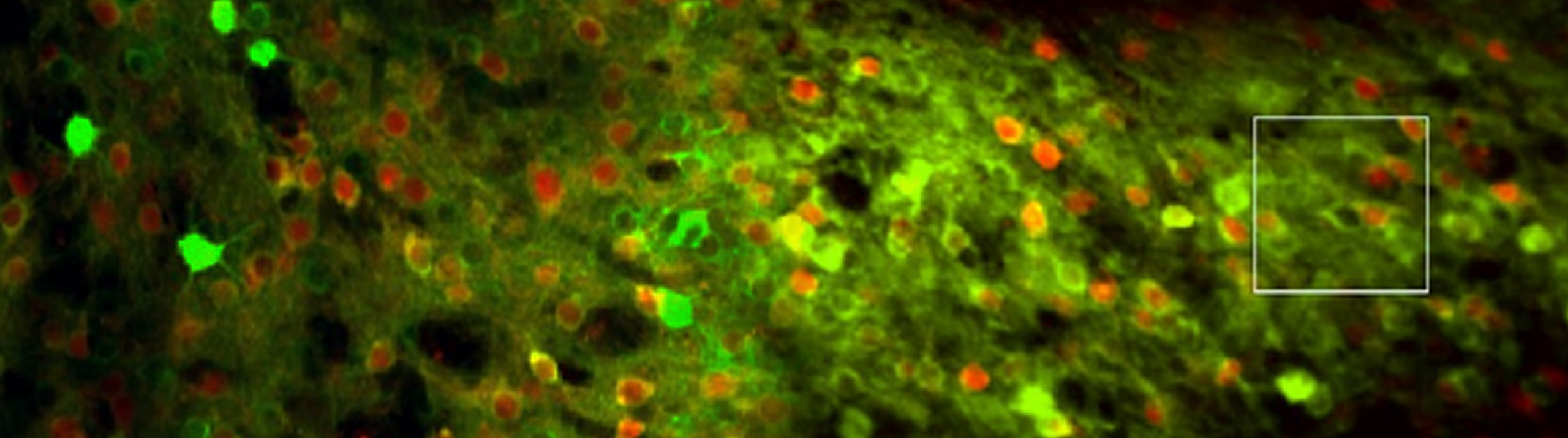
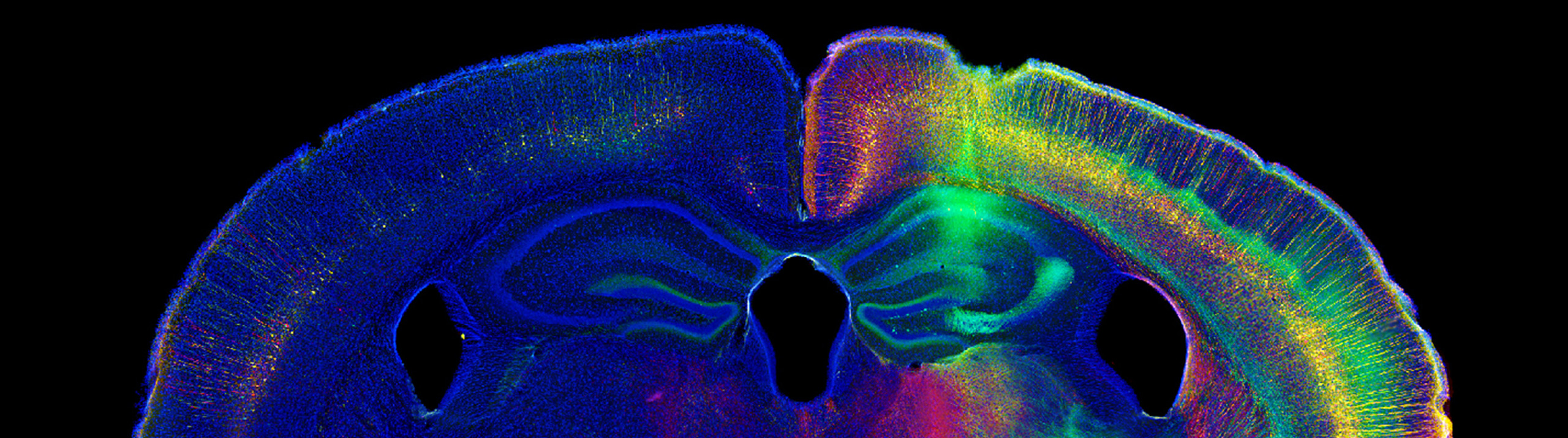
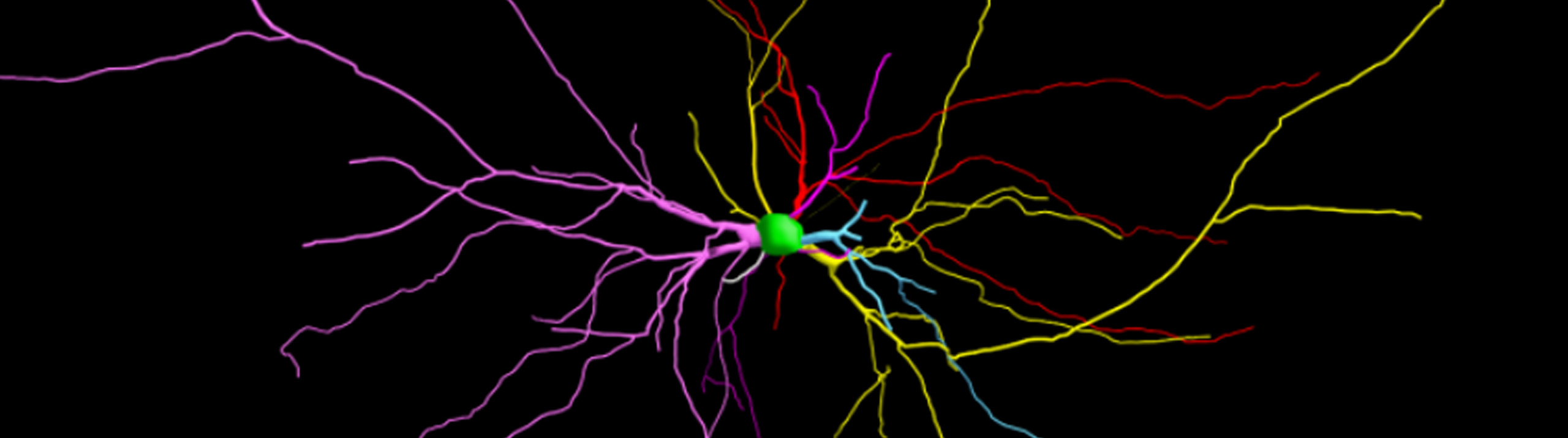
History is being made at George Washington University’s Laboratory for Evolutionary Neuroanatomy, and Stereo Investigator is playing a part. Using Stereo Investigator to count neurons, estimate axon fiber length, and quantify cellular volumes, Dr. Chet C. Sherwood and his team are carrying out "detailed comparisons of neural phenotypes between humans and our closest relatives, the great apes." A recent focus at the lab is the emergence...
Read MoreMBF Products & Service Solutions
Myelin, which insulates axons in the central nervous system is produced by oligodendrocytes. But not all oligodendrocytes are equal. Led by Dr. Jonathan Vinet of the Université Laval in Quebec, scientists have identified three different types of oligodendrocytes in the mouse hippocampus: "ramified," "stellar," and "smooth." Each type displayed varying morphological characteristics, mainly in shape, volume, and branching behavior, which led the researchers to believe that the...
Read MoreThere may be more evidence that schizophrenia results from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. One of these hereditary influences may be an impaired ability to synthesize the antioxidant glutathione (GSH), which results in oxidative stress, according to a study conducted by scientists at the University of Lausanne in Switzerland. By observing mice with a GSH deficit, Dr. Kim Q. Do and her team determined...
Read MoreUniversity of Maryland School of Medicine researchers have used Neurolucida since it was in its embryonic stages in the 1960s. Now, nearly a half-century later, the Department of Anatomy and Neurobiology continues using Neurolucida in their research, as outlined in a recent study concerning the organization of the olfactory system. Dr. Michael Shipley and his team collaborated with scientists from Hungary and Japan on the paper...
Read MoreAlzheimer's disease is the most common form of dementia. Most cases occur in people over 65, and are not genetically inherited. Roughly five percent of Alzheimer's patients suffer from familial Alzheimer's disease (FAD), an uncommon form that tends to strike sooner, and is related to a genetic predisposition - most commonly, a mutation in the presenilin 1 gene (PS1). A recent study, led by Dr. Miguel...
Read MoreBirds and mammals hear binaurally, hearing sounds through two ears. Binaural hearing allows them to determine which direction a sound came from—a pivotal element of survival. Doctors Armin H. Seidl, Edwin W. Rubel, and David M. Harris of Seattle’s Virginia Merrill Bloedel Hearing Research Center at the University of Washington recently published a study in the Journal of Neuroscience that may encourage scientists to think in...
Read MoreIf you start smoking as a teen, it’s much harder to quit. University of Vermont Neurobiologist Rae Nishi wants to find out why. And thanks to a $1 million Challenge Grant, Nishi and her team will be able to further study the way adolescent brains react to nicotine. The grant is one of 200 National Institute of Health grants allocated by the American Recovery and Reinvestment...
Read MoreThe developing and adult central nervous system of the mouse is complex and large. NIH Neuroscientist Dr. Charles Gerfen uses Neurolucida and NeuroInfo to collect, display, and share virtual slides with the research community. Recently, Dr. Gerfen requested software enhancements to better allow him to categorize and use his virtual slide data in mouse brain testing. We were happy to comply. Dr. Gerfen explains how he uses...
Read MoreThousands of people in the United States have spinal cord injuries (SCIs), with associated loss of movement and sensation below the site of the injury. Neural and glial cell transplants into research animals after SCI have correlated with recovery of function. The improvement may be caused by the transplanted cells; it’s thought that remyelination by the transplanted glial cells is the main reason for the...
Read MoreNeurolucida is used for reconstruction and morphometric analysis of neurons and anatomical regions of interest. Neurolucida can also be used for quantitative and qualitative analysis of dendritic spines. Spines are small, often bulbous protrusions that emerge from the dendritic shaft. They are the main site of excitatory synapses in the brain [1], and they range in length from 0.001 to 1mm and range in diameter...
Read More